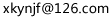八种常用时态的主动和被动的结构
一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时等常用时态。
主动是由主语主动发出的动作,如:I
go
to
school
everyday.相反被动结构不是自主的,如:He
was
fired.
A.一般现在时
1.I love cat
cat is loved by me
2.I love dog
dog is loved by me
3.I love pig
pig is loved by me
4.I love monkey
monkey is loved by me
5.I kill you
you are killed by me
6.I rape you
you are raped by me
7.he kills you
you are killed by him
8.pig loves you
you are loved by pig
9.cat loves you
you are loved by cat
10.idiot kills you
you are killed by idiot
B.现在进行时
1.I am loving cat
cat is being loved by me
2.I am loving dog
dog is being loved by me
3.I am loving birds.
birds are being loved by me
4.I am killing you
you are being killed by me
5.He is killing you
you are being killed by him
6.you are enjoying your computer
your computer is being enjoyed by you
7.your teacher is kicking your ass
your ass is being kicked by your teacher
8.you are writing a paper.
a paper is being written by you
9.you are reading a book
a book is being read by you
10.Tom is loving Jane
Jane is being loved by Tom
C.一般将来时
1.I will love pig
pig will be loved by me
2.I will love cat
cat will be loved by me
3.i won't kill you
you won't be killed by me
4.i won't love pig
pig won't be loved by me
5.i won't love cat
cat won't be loved by me
6.you will capture him
he will be captured by you
7. he will capture you
you will be captured by him
8.I will read a book
a book will be read by me
9.you will mend a computer
a computer will be mended by you
10.police will hate you
you will be hated by police.
D.一般过去式
1.I loved cat
cat was loved by me
2.i loved mammal
mammal was loved by me
3.i loved women
women were loved by me
4.i loved gay
gay was loved by me
5.you loved gay
gay was loved by you
6.you read a book
a book was read by you
7.you killed dog
dog was killed by you
8.you killed cat
cat was killed by you
9.you read a paper
a paper was read by you
10.you used a pen.
a pen was used by you.
E.现在完成时
1.you have loved a dog
a dog has been loved by you
2.you have loved a cat
a cat has been loved by you
3.you have loved mammal
mammal has been loved by you
4.you loved birds
birds have been loved by you
5.you have loved baidu
baidu has been loved by you
6.you have loved gay
gay has been loved by you
7.you have loved naruto
naruto has been loved by you
8.you have loved bleach
bleach has been loved by you
9.you have dropped your ball
your ball has been dropped by you
10.you have read a book
a book has been read by you
F.过去进行时
1.you were loving pig
pig was being loved by you
2.you were loving birds
birds were being loved by you
3.you were loving mammal
mammal was being loved by you
4.you were loving 727960629
727960629 was being loved by you
5.you was killing 727960629
727960629 was being killed by you
6.you was fucking 727960629
727960629 was being fucked by you
7.you was raping 727960629
727960629 was being raped by you
8.you was sucking 727960629 's ball
727960629' ball was being sucked by you
9.you was dumping garbage
garbage was being dumped by you
10.you was shooting him
he was being shot by you
G.过去将来时
1.you would love him
he would be loved by you
2.you would love pig
pig would be loved by you
3.you was going to kill him
he was going to be killed by you
4.you were going to shake his head
his head was going to be shaken by you
5.you were going to suck his ball
his ball was going to be sucked by you
6.your mom was going to enter hell
hell was going to be entered by your mom
7.your mom was going to kill him
he was going to be kill by you.
8.your mom would kill your dad
your dad would be killed by your mom
9.you were going to kill your friends.
your friends were going to be killed by you.
10.you were going to write 160 sentences
160 sentences were going to be written by you.
H.过去完成时
1.you had loved your pig
your pig had been loved by you
2.you had loved your cat
your cat had been loved by you
3.you had loved your bird
your bird had been loved by you
4.you had loved your family
your family had been loved by you
5.you had killed your family
your family had been killed by you
6.you had liked your family
your family had been liked by you
7.you had eaten your dog
your dog had been eaten by you
8. you had eaten your cat
your cat had been eaten by you
9.you had killed your mom
your mom had been killed by you
10. you had killed your dad
your dad had been killed by you
P.S:终于写完了!
这八种常用时态的主动和被动的结构如下:
一、一般现在时
1.概念:指经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2.时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.
二、一般过去时
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
三、现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
四、过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
五、现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years, etc.
六、过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),by the time...,etc.
七、一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
八、过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
在语法里,时或时态表示行为发生的时间和说话时的关系。一般分为过去式、现在式、将来式,通常也有与表示动作进行或终止的进行式和完成式等体貌一起相连用的情况。
时态连同语气、语态、体貌和人称为动词形式至少可能能够表现出的5种语法特性。
有些语言,没有时态的使用,如分析语的中文,但必要时,仍有时间副词的辅助。也有些语言,如日文,形容词的词形变化能表达出时间上的资讯,有着类似动词的时态性质。还有些语言,如俄文,一个单词就能表现出时态和体貌。
英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
一般过去时与现在完成时的转换 在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。但是,可用别的表达方式:
①瞬间动词用于“一段时间 + ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
②瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
③瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间 + since + 一般过去时”的句型,请看:A. He joined the League two years ago. B. He has been in the League for two years. C. It is two years since he joined the League. D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
一般现在时与现在进行时的转换在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如at work(在工作),at school(上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。请看:Peter is at work,but Mike is at playPeter is working,but Mike is playing.
现在进行时与一般将来时的转换在现在进行时态中go,come,leave,start,arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。如:I am coming,Mum! 意为“我就来,妈妈!”请看:The train is leaving soon. The train will leave soon.
以上内容参考:百度百科--时态
八种时态 主动语态 被动语态 一般现在时 (经常, 反复, 爱好, 特点, 条件, 真理) do; does am;is;are done。
一般过去时 (过去发生的事, 不强调现在的结果) did; -ed was;were done。
一般将来时 (将要发生的事) will do will be done。
现在进行时 (现在正在发生的事) am;is;are doing am;is;are being done。
过去进行时 (当时正在发生的事) was;were doing was;were being done。
现在完成时 (过去发生的事, 强调现在的结果) have;has done have;has been done。
过去完成时 (过去完成的事;过去以前发生的事) had done had been done。
过去将来时 (过去将要发生的事) would do would be done。
八种时态:
• He is always ready to help others. 一般现在时。
She often came to help us in those days.一般过去式。
• He is doing his homework now. 现在进行时。
• At that time she was doing her homework.过去进行时。
• I've written an article.现在完成时。
• By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books 。过去完成时 • It is going to rain.一般将来时。
• I asked who was going there. 过去将来时。
一、一般现在时
1.概念:指经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2.时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.
3.基本结构:动词+ 原形 (如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S)。
4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6.例句:. It seldom snows here.
He is always ready to help others.
Action speaks louder than words.
7.特殊用法:一些动词可用一般现在时来表达现在进行时:
verbs of the senses: hear,see,taste,smell.
verbs of the thinking: believe,know,mean,realize,think,remember.
verbs of the linking: dislike,fear,hate,like,love,want.
verbs of the possession: belong,have,own,possess.
二、一般过去时
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
3.基本结构:含有Be动词主语+was/were+形容词或者名词......
不含有be动词:主语+动词过去式+......
4.否定句:带be:主语+was/were not+形容词或者名词+......
不带be:主语+didn't+动词原形+......
5.一般疑问句:含be动词was或were放于句首;
不含be动词用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词原型。
Did+主语+动词原形+……?
6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.
I didn't know you were so busy.
She sang a song of Lin Feng yesterday.
三、现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
3.基本结构:Be动词(am/is/are)+doing
4.否定形式:Be动词(am/is/are)+not+doing.
5.特殊疑问句:把be动词放于疑问词的后面。
6.例句:How are you feeling today?
He is doing well in his lessons.
7. 一般表示位移的词如leave fly arrive go come. 等用现在进行时表将来。
I am flying Beijing next week .表示我下周即将飞往北京。
He is leaving for Beijing tomorrow. 他明天即将去北京。
8.现在进行时就是一个动词后面加ing
四、过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构:was/were + doing
4.否定形式:was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit.
When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
五、现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:have/has + done
4.否定形式:have/has + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:have或has提前。
6.例句:I've written an article.
It has been raining these days.
六、过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),by the time...,etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.
By the end of last month,we had reviewed four books
七、一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:am/is/are + going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:am/is/are + not+going to;will/shall+not(will适用于所有人称,shall只用于第一人称)
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies.
It is going to rain.
I think he will be back soon
八、过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:was/were + going to + do;would/should + do.
4.否定形式:was/were + not + going to + do;would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day.
I asked who was going there .
以上内容参考:百度百科-八大时态
一) 一般现在时
被动语态:
主语+be+动词过去分词+by(加宾格)
eg:He waters the flowers every day.
The flowers are watered by him every day.
二)一般过去时
被动语态:主语+was\were+动词过去分词
eg:He took care of his little brother yesterday.
His little brother was taken care of by him yesterday
三)现在进行时
被动语态:主语加am\is\are加being加动词过去分词
例句:Helen is writing a letter.
A letter is being written by helen.
四)过去进行时
被动语态:主语+was\were+being+动词过去分词
eg:He was making a model plane.
A model plane was being made by him.
五)现在将来时
主语+be going to be+动词过去分词
eg:They will clean the windows tomorrow.
The windows will be cleaned by them.
六)过去将来时
主语+was/were going to be +动词过去分词
eg:He said he would finish the project by the time we reached there.
He said the project would be finished by the time we reached there.
七)现在完成时
主语+have/has + been+动词过去分词
eg:he has sung a nice song.
A nice song has been sung by him.
八) 过去完成时
主语+had +been +动词过去分词
eg:He had posted the letter .
The letter had been posted by him.
英语 各时态 的 被动语态 请将各时态的动词结构先写出主动的再写出被动的 英语应该共8个时态 被动语态的时态由被动结构“be+过去分词”中的动词be来体现,其基本结构和用法如下: (1)一般现在时的被动语态:am [is,are]+过去分词 (2) 一般过去时的。
初中英语的八种时态和被动语态
答:语态也是动词的一种形式,表示主语与谓语之间的关系。英语有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态People .被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者,.(II)被动语态的构成 被动语态的形式是由“助动词be动词的过去分词”构成。助动词be随着主语的人称,数,时态和语气的不同而变化。各种时态的被动语态形式如下:1.注:...
求英语中各种时态的主动语态和被动语态 最好列个表
答:被动语态:1.一般现在时 is\am\are+P.P(过去分词)2.一般过去时 was\were+P.P 3.一般将来时 will be+P.P 4.现在进行时 is\am\are+being(固定不变)+P.P 5.过去进行时 was\were+being(固定不变)+P.P 6.现在完成时 have\has been+P.P 7.过去完成时 had been+P.P 主动语态:主动...
英语中8种时态主动和被动的表达方式是哪
答:一般现在时do-is/are done 现在进行时is/are doing-is/are being done 现在完成时has/have done-has/have been done 一般过去时did-was/were done 过去进行时was/were doing-was/were being done 过去完成时had done-had been done 一般将来时will do-will be done 将来进行时will be doing-...
写出下列各种时态的构成: 主动语态 被动语态 1.一般现在时: 2.一般过...
答:以助动词do为例 1.一般现在时:主动:do/does 被动:am/is/are done 2.一般过去时:主动:did 被动:was/were done 3.一般将来时:主动:will/shall do 被动:will/shall be done 4.现在进行时:主动:am/is/are doing 被动:am/is/are being done 5.现在完成时:主动:have...
初中英语八大时态被动语态结构 一定是结构 谢谢
答:被动语态 英语动词有主动语态和被动语态之分。在主动句中,动词的主语是执行动作的人或物。在被动句中,主语是动作的承受者。在英语中被动态用得很普通,这样做可以避免用不明确的词作主语,或是将说话的重点放在事件而不是造成该时间的人或物上。被动语态的构成:be+过去分词。过去分词不一定指过去。
有谁能把我总结一下英语的八大时态是哪八大时态,他们的被动形式又是如何...
答:其实英语共有十六种时态,但我们平时比较常用的只有八种,如下:1.一般现在时: 主语+do/does(现在分词)e.g We clean the room every day. The room is cleaned by us every day.2.一般过去时: 主语+did e.g We cleaned the room just now. The room was cleaned by us just now.3....
初中的所有时态和被动语态谁给总结一下
答:Ⅰ. 初中英语八种时态归纳复习 时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,广大初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,下面我们就归纳复习一下这几种时态。一、一般现在时:概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year,...
急求!英语中各个时态的主动语态和被动语态的结构
答:一般现在时:主语+实义动词(主语是第三人称代词单数,实义动词用第三人称单数形式;其余人称代词无论单复数,实义动词都用原型)eg.I go to school on foot.He goes to school on foot.You go to school on foot.We go to school on foot.现在进行时:主语+be(am/is/are)+动词ing形式 ...
英语八大时态结构和八大时态的被动语态结构
答:如果像老师上课时那样写出:be+实意动词+ing 这样的结构可能不够清楚易懂,还不如举些例子来说明:一般现在时:I water the flowers. The fowers are watered .现在进行时:I am watering the flowers. The flowers are being watered.一般过去时:I watered the flowers. The flowers were watered...
急求!英语中各个时态的主动语态和被动语态的结构
答:例如:He opened the door.他开了门。(主动句)The door was opened.门被开了。(被动句)二、被动语态的构成 被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。人称、数和时态的变化是通过be的变化表现出来的。现以teach为例说明被动语态在各种时态中的构成。一般现在时:am/is/are+taught 一般...